Ready-to-Use EMERPHED® in 3 simple steps:
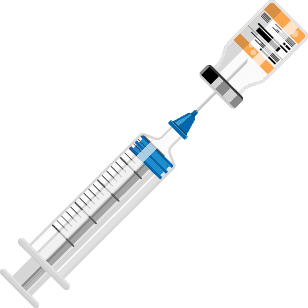
Step 1
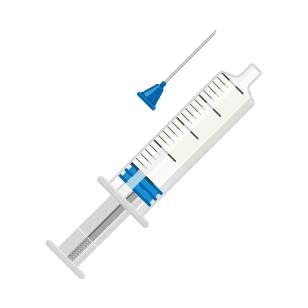
Step 2
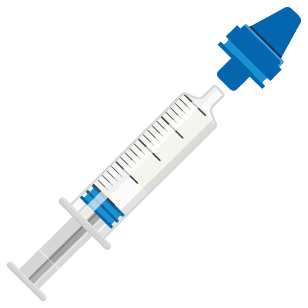
Step 3
Aligns with standardization recommendations of patient safety and professional organizations: APSF,1 ASHP.2


—VS—
DELAYS and DRAWBACKS of TVSP (traditional vial and syringe process):
Risk for error if using concentrated ampule

Step 1

Step 2
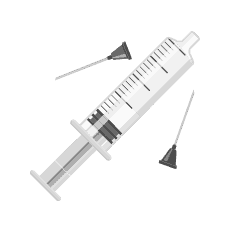
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5

Step 6
Step 7
Risk for error if using concentrated vial
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3

Step 4
Step 5
FDA warns of risk with the use of products that require compounding.

Nearly half of errors with IV medications occur during preparation or administration³

At-risk practices include number of steps required, syringe-to-syringe transfer, unnecessary dilution, and use of saline flush syringes to dilute IV medications³,⁴
Ready-to-use, manufacturer-prepared products are viewed as the drug delivery of choice.


Recommended to help reduce errors while
maintaining efficiency3
References: 1. Recommendations for improving medication safety. Consensus from four work groups at the 2018 APSF Stoelting Conference on Medication Safety. Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation. https://www.apsf.org/medication-safety-recommendations/. Accessed November 19, 2019. 2. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. ASHP guidelines on preventing medication errors in hospitals. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2018;75:1493–1517. 3. Hertig J, Degnan D, Scott C, et al. A comparison of error rates between intravenous push methods: a prospective, multisite, observational study. J Patient Saf. 2018;14(1):60-65. 4. Burger M, Degnan D. Comparative Safety, Efficiency, and Nursing Preference Among 3 Methods for Intravenous Push Medication Preparation: A Randomized Crossover Simulation Study. J Patient Saf. 2019;15(3):238-245.
What important safety infomation should I know?
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
EMERPHED® can cause pressor effects with concomitant use with oxytocic drugs. Can also cause tachyphylaxis with repeated administration of ephedrine.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions during treatment: nausea, vomiting, and tachycardia.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Nexus Pharmaceuticals at (855) 642-2594 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Can include: interactions that augment pressor effect; interactions that antagonize the pressor effect; guanethidine; rocuronium; epidural anesthesia; theophylline; cardiac glycosides.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdose of EMERPHED® can cause a rapid rise in blood pressure. In the case of an overdose, careful monitoring of blood pressure is recommended. If blood pressure continues to rise to an unacceptable level, parenteral antihypertensive agents can be administered at the discretion of the clinician.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ephedrine Sulfate injection is an alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonist and a norepinephrine-releasing agent that is indicated for the treatment of clinically important hypotension occurring in the setting of anesthesia.
For more information, see full Prescribing Information.
EPH-137-v2
